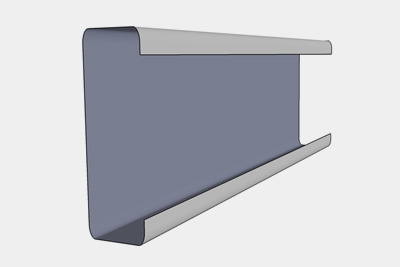
C Purlins are horizontal structures that are used to support the load from the roof deck or the sheathing. The plane surface of this purling on one side has made it a preferred material for cladding due to its easy installation on concrete structures or steel. Our range purlins are light in weight and perfect for simple span construction.
Secondary Structure
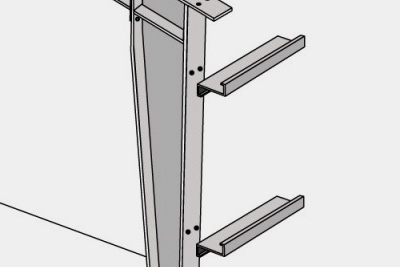
Secondary structural framing refers to purlins, girts, eave struts, wind bracing, flange bracing, base angles, clips and other miscellaneous structural parts.
Purlins, girts and eave struts are cold formed steel members which have a minimum yield strength of 345 MPa (50,000 psi) and will conform to the physical specifications of ASTM 572 (Grade 50) or ASTM A653 (Grade 50) or equivalent.
Secondary members have two other functions:
Act as struts that help in resisting part of the longitudinal loads that are applied on the building such as wind and earthquake loads Provide lateral bracing to the compression flanges of the main frame members thereby increasing frame capacity.
Z Purlins are made using cold-formed or rolled sheets for supporting roof. The flexible shape of these beams facilitates various designs solutions. These purlins are extensively used in huge roofing solutions such as godowns, workshops, industrials sheds and many more. The range is known for saving upto 50% on structural sheet in comparison with hot rolled angles. Our purlins are crisp and clean in design and do not allow the scope of inaccurate lengths.
The wall girts are cold formed Z shape members, consisting of various thickness and variable depth depending upon the design. The wall girts plays a vital role in the secondary framing systems, which form the pre-engineered structure combined with the primary framing systems and the connectable sheeting. These are fixed to the outer flange of the side wall columns with the help of clips bolted to the column and girt web bolted to the clips.
Eave struts are 200 mm deep with a 104 mm wide top flange, a 118 mm wide bottom flange, both are formed parallel to the roof slope. Each flange has a 24 mm stiffener lip. These are located along the sidewall; at the intersection of the planes of the roof and wall. It is constructed from cold formed C-Section and is rolled to suit the roof slope. This member transmits longitudinal wind force on the end walls from roof brace rods to wall brace rods.
These are long span load carrying trusses suitable for direct support of floors and roof decks in the buildings. The system consists of crimped angles welded to the top and bottom chords.
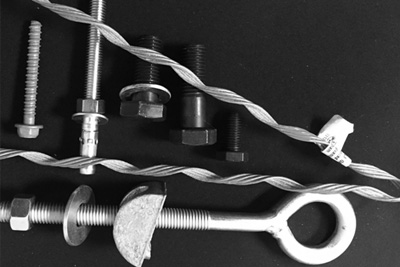
Cable bracing is made of extra high strength seven strand cable and can be designed to accommodate any length to ensure the stability of the building against forces in the longitudinal and lateral direction due to wind, cranes and earthquakes. It is made of a cable which is forged into a rod terminal and this arrangement is then fixed on a structure using a hill side washer, nut washer and a nut.